How VR is changing the healthcare market
Market analysis and statistical data reveal just how much the explosion in VR investment is transforming the healthcare industry.
Virtual reality (VR) technology has emerged as a powerful tool in the healthcare industry, transforming the way patients are cared for, medical professionals are trained, and data is applied towards innovation and growth.
VR in healthtech isn't just making waves — it's riding a veritable tsunami of growth. But it’s not solely about what the charts tell us. Go a little deeper into VR technology in the healthcare industry, and you’ll find a host of cutting-edge applications, like therapists using VR to augment patient care and doctors collaborating with patients outside of the typical hospital environment.
It’s a technological future that the healthcare industry isn’t just anticipating, but actively shaping.
Market overview
A strong year-over-year growth rate demonstrates just how much of a foothold virtual reality is gaining in healthcare. With applications throughout the patient care process and in healthcare education, it’s no wonder that VR has found use cases across healthcare environments.
The projections reflect surging ubiquity: Virtual reality in healthcare is expected to grow globally from $3.1B industry in 2023 to $25B by 2030, at a CAGR of 34.9 percent during the forecast period — or by other measures, an extremely robust 39.4 percent from 2023 to 2030.
Meanwhile, Deloitte reports that the VR portion of the healthtech market made $4.7B in revenue in 2022, and that it is projected to make a massive leap to over $7 billion by the end of 2023 — a nearly 50 percent increase in just one year.
Not shabby indicators of how adoption and demand for VR solutions in healthcare is growing.
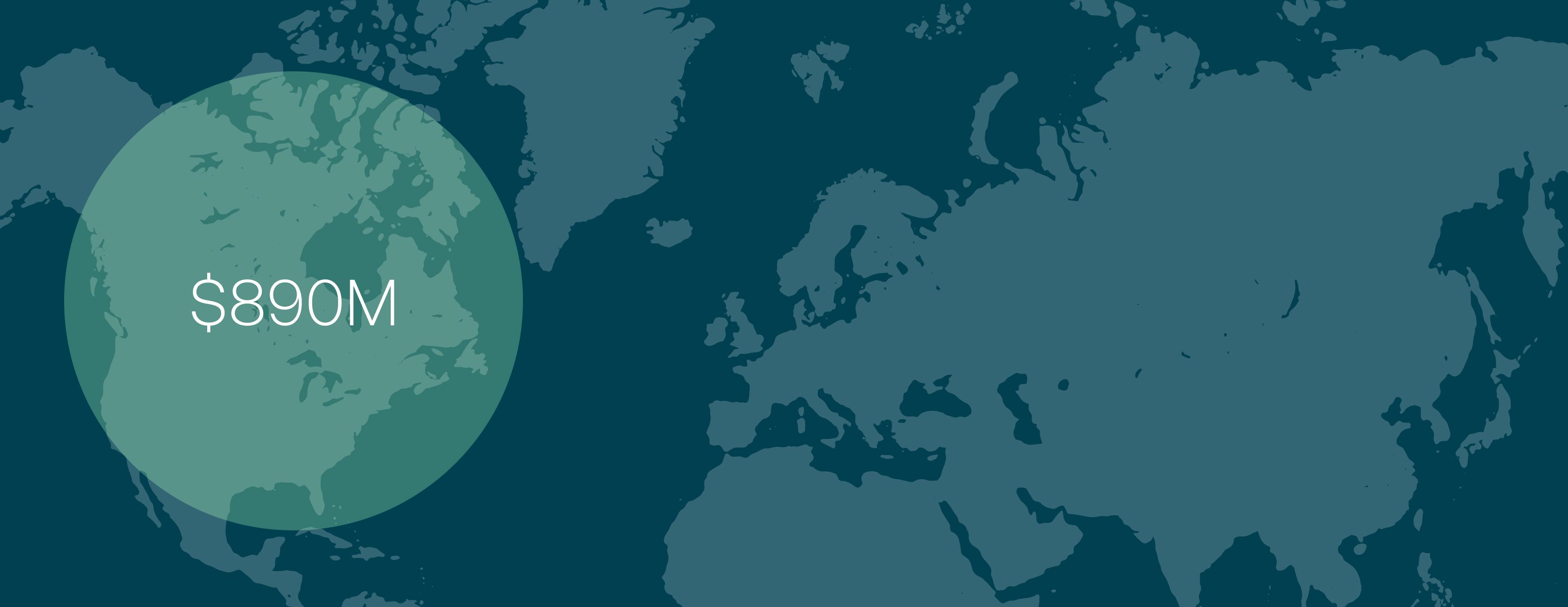
By region
The North American VR healthcare market reached $890M, and is only expected to continue growing to hold most of the global market. Nevertheless, the Europe and Asia-Pacific markets are also expected to continue to grow.
These regions have proactively integrated VR technology into healthcare, opening doors to numerous advancements and opportunities.
By segmentation
Diving into the distinct segments of the VR healthcare market — software, hardware, and content — one can spot a consistent trend of innovation. Hardware accounts for about half (49.4 percent) of the global VR in healthcare market.
This is consistent with findings across the broader VR market: One report finds that 90 percent of the increased revenue associated with growth in the global virtual reality industry will come from hardware sales, with 14 million headset units expected to sell in 2023. This coincides with actively-used VR headsets reaching 22 million in 2023 — a nearly 50 percent increase from 2022.
And, Apple’s headset, with its steep entry pricing and high-end components, isn’t poised to drive sales when the hardware begins shipping in early 2024, the market buzz is expected to energize the sales of other vendors’ headsets in the short term — to the tune of a 22.1 percent CAGR in AR/VR headsets between 2022 and 2027. It’s safe to say that Apple’s entry into the headset market will inevitably lift the entire AR/VR industry in the long term.
What accounts for that final 10 percent of the virtual reality industry’s revenue growth? VR software and content, which could see revenue of approximately $700M. What’s noteworthy across the virtual reality industry — and specifically VR in healthcare — is how maturing product quality has aligned with better cost-efficiency. This has not only made advanced VR devices more accessible but also underscores acknowledgment of VR's pivotal role in modern medical practices.
Applications of VR in healthcare
The explosive growth and massive investment in VR healthtech is far from speculative. Rather, it’s a reflection of overwhelmingly positive results across the industry, from providers and patients to students and administrators.
Patient care management
VR technology has demonstrated exceptional results in patient care management. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine in 2021 found that VR-based interventions can significantly reduce pain and anxiety levels in patients undergoing medical procedures.
Moreover, VR has been proven to enhance the effectiveness of pain management strategies, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Virtual reality has proven to be helpful not just in patient care itself, but also the accessibility of patient care. And healthcare executives are all in:
agree that augmented and virtual reality are removing the hurdles to care access
agree that augmented and virtual reality will create a new foundation for interaction, communication, and information
believe it’s important for their organization to leverage augmented and virtual reality solutions
agree that extended reality will be widespread and impact virtually every industry over the next five years
Patients are on board, too. This wasn’t always the case. While virtual access to care was stalled prior to COVID-19, the pandemic spurred widespread adoption — and attitude shifts — about receiving care digitally. Sixty-two percent of patients are now open to virtual health and wellness advisories.
The financial benefits of VR applications in patient care management allow healthcare providers to reduce overhead and provide greater value. Hospitals and healthcare facilities that have implemented VR solutions have reported reduced costs associated with medication and traditional pain management methods.
Plus, with every VR intervention that eliminates the need for a more expensive pharmacological intervention, hospitals are able to proactively eliminate additional costs.
One of the biggest winners of the healthtech metaspace race is VR in telemedicine and remote patient care. With more people than ever relying on healthcare in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, virtual applications have made medical care more flexible and accessible.
This kind of VR integration allows healthcare professionals to remotely monitor patients, provide virtual consultations, and deliver personalized care, which is especially valuable in rural and extremely remote areas where access to specialized healthcare and healthcare providers is limited.
Medical education and training
VR in medical education has proven to be extremely effective for the education and improvement of medical students and professionals. A study by UCLA found that learners trained with VR programs showed higher levels of retention and substantially improved performance compared to traditional training methods.
Specifically, that study found that VR in surgery training programs led to an improvement in performance of 230 percent compared to students not trained with those same VR applications.
This technology provides a realistic and immersive learning environment, enabling medical students to gain hands-on experience in a controlled but realistic setting.
Another review found improved learning and higher accuracy in medical practice by people trained through VR in a majority of studies.
Investments in VR-based education and training programs have surged in recent years. In light of initial results, universities and hospitals worldwide are adopting VR to enhance the training of students and employees.
In addition to improving the quality of education for future medical professionals, this also means a major influx of investment from private and government medical facilities, further bolstering the market prospects for VR in healthcare.
Rehabilitation and therapeutic treatments
VR has emerged as a game-changer in rehabilitation and therapy procedures. It’s proven to be particularly effective in speech therapy and language rehabilitation, aiding patients in both improving and rebuilding communication skills.
VR vision therapy has already been shown to be very effective as part of a treatment plan for common vision conditions such as cross-eye or lazy eye. The launch of the Vision Therapy for VR app on Steam has already made a strong case for the DTC marketability of vision — and other forms of — therapy.
Physical therapists have embraced VR as a valuable tool for treating patients and for supporting better self-guided therapies for patients at home. These programs assist patients in the rehabilitation of motor skills, balance, and coordination. The immersive nature of VR allows patients to engage in interactive exercises and activities that promote movement, leading to improved physical functioning and overall recovery.
And then there’s virtual reality exposure therapy (VRET), which combines VR technology with proven exposure therapy techniques to help patients face their fears in a controlled, safe environment. After discussing the cause of their trauma with a therapist, patients experience a custom VR environment that mimics their trauma or phobias complete with multisensory stimulations — think someone with a fear of flying experiencing the sounds and sensations of turbulent aircraft in an environment that is not actually an aircraft.
The result? Patients can confront and gradually desensitize themselves to triggers. VRET offers a flexible alternative to traditional therapy, improving access to treatment, allowing care from virtually any location, and customizing exposure levels.
Future Impacts of VR on the healthcare market
The integration of VR in healthcare is expected to have transformative effects on the market: It will streamline patient care, improve diagnostic accuracy, and enhance surgical precision. More importantly, though, the continued adoption of VR applications in healthcare will reduce overall costs and improve access to care, making it possible for even more people to receive treatments they need and improving quality of life.
As VR technology becomes more advanced and accessible, it's likely that we will see a rise in patient engagement and satisfaction, too. Patients may become more actively involved in their care and have a better understanding of their health conditions, thanks to both the immersive, visual nature of VR and the lowered barriers for receiving care.
Furthermore, the use of VR in mental health treatment could revolutionize therapy and offer cost-effective, stigma-free solutions to patients worldwide. By being able to access treatment in their own homes, patients could overcome the barriers to mental health care, such as lack of transportation or fear of social stigma from receiving care.
VR Development in Healthcare
As the healthcare industry's demand for VR solutions grows, we will likely see a corresponding increase in the need for VR developers. The scarcity of experienced VR developers means that the cost of hiring such talent in-house could rise considerably. For most healthcare organizations, partnering with dedicated teams for VR integration and development may be the most cost-effective solution, ensuring access to reliable VR development expertise.
To meet the increasing demand for VR in healthcare, universities and colleges are launching dedicated VR programs. These specialized courses equip future VR developers to cater to needs in healthcare and beyond.
Faster, more efficient, and accessible medical education
VR is transforming the landscape of medical education. It offers immersive, hands-on training for medical students, enabling them to practice procedures in a risk-free environment. Such training bolsters their skills and confidence long before they step into an operating room.
Furthermore, the scalability of VR instruction means that it could alleviate the constant shortage of healthcare professionals. Imagine a world where anyone, anywhere, can access high-quality medical training through VR. This could lead to improving access to medical education, with profound impacts on global health outcomes.
Healthcare’s virtual realities
Virtual reality offers enormous value across industries; the applications and innovations within the healthcare industry can’t be overstated. Its benefits in education, treatment, administration, and accessibility are all immediate, tangibly measured trends that are charting up and fast. And like any solution with demonstrable results, the interest and investment for it is already rapidly increasing.
The statistics reflect this dynamic change in healthcare, but what remains to be seen is what — or, more directly, who — will be directing it. With a wealth of market research, we can say with absolute confidence that VR will be a major force in the immediate, short-term, and long-term future of healthcare both as an industry and as a part of society.
But with so much innovation only just beginning to take shape, the major players in this developing market will be those who account for its developing trend: finding cost-effective means of moving to market quickly, which means securing experienced VR developer talent.




